
Breaking News
Who Was The Biggest Antisemite In 2025?
 Putin residence attack jeopardizes US security guarantees
Putin residence attack jeopardizes US security guarantees
 NY Times Expose: CIA Fights Russia – Trump's Peace Deal Runs on Illusion
NY Times Expose: CIA Fights Russia – Trump's Peace Deal Runs on Illusion
 Fearless Predictions, Ten Key Events to Expect in 2026
Fearless Predictions, Ten Key Events to Expect in 2026
Top Tech News
 Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Liquid metal feeds Stanford's new high-voltage flow battery
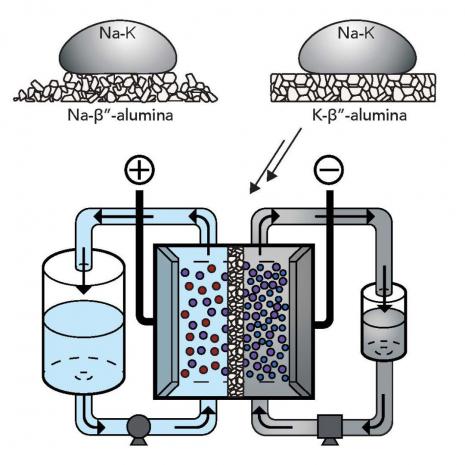
Engineers at Stanford have developed a new type of flow battery that might be scalable, safe, efficient and inexpensive, using a metal mixture that remains liquid at room temperature.
In a flow battery, the cathode and anode are in fluid form and are kept in external tanks, to be pumped into the main cell of the battery when needed. There, the two liquids are separated by a membrane that selectively allows them to exchange electrons to either charge or discharge the energy.
These devices may be able to store huge amounts of energy in future, but the chemicals used are often toxic, expensive, and difficult to handle. The Stanford team designed the new flow battery to overcome those problems, using a unique combination of materials.



