
Breaking News
 Nationwide Tax Competition Heats Up as Missouri Governor Calls for Zero Income Tax
Nationwide Tax Competition Heats Up as Missouri Governor Calls for Zero Income Tax
 Matthew McConaughey Trademarks Himself to Fight AI Misuse
Matthew McConaughey Trademarks Himself to Fight AI Misuse
 More Americans are surviving cancer - even the deadliest ones
More Americans are surviving cancer - even the deadliest ones
 Former CEO of Venezuelan Oil Company CITGO Held Hostage by Nicolas Maduro for Five Years...
Former CEO of Venezuelan Oil Company CITGO Held Hostage by Nicolas Maduro for Five Years...
Top Tech News
 Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
 World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
 New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
 Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
 Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
 Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
 US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
 Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
No stethoscope for pain: Scientists seek real way to measure
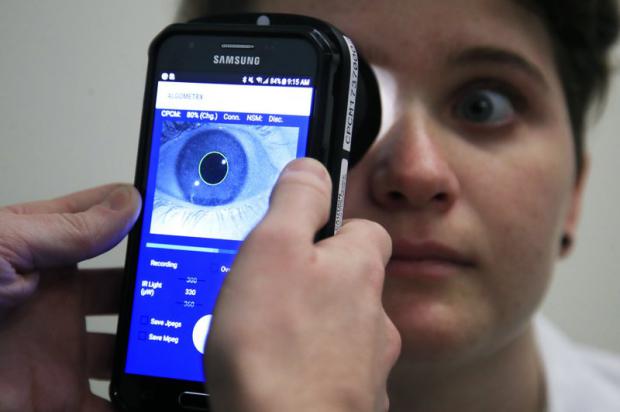
WASHINGTON (AP) — Is the pain stabbing or burning? On a scale from 1 to 10, is it a 6 or an 8?
Over and over, 17-year-old Sarah Taylor struggled to make doctors understand her sometimes debilitating levels of pain, first from joint-damaging childhood arthritis and then from fibromyalgia.
"It's really hard when people can't see how much pain you're in, because they have to take your word on it and sometimes, they don't quite believe you," she said.
Now scientists are peeking into Sarah's eyes to track how her pupils react when she's hurting and when she's not — part of a quest to develop the first objective way to measure pain.
"If we can't measure pain, we can't fix it," said Dr. Julia Finkel, a pediatric anesthesiologist at Children's National Medical Center in Washington, who invented the experimental eye-tracking device.
At just about every doctor's visit you'll get your temperature, heart rate and blood pressure measured. But there's no stethoscope for pain. Patients must convey how bad it is using that 10-point scale or emoji-style charts that show faces turning from smiles to frowns.
That's problematic for lots of reasons. Doctors and nurses have to guess at babies' pain by their cries and squirms, for example. The aching that one person rates a 7 might be a 4 to someone who's more used to serious pain or genetically more tolerant. Patient-to-patient variability makes it hard to test if potential new painkillers really work.
Nor do self-ratings determine what kind of pain someone has — one reason for trial-and-error treatment. Are opioids necessary? Or is the pain, like Sarah's, better suited to nerve-targeting medicines?
"It's very frustrating to be in pain and you have to wait like six weeks, two months, to see if the drug's working," said Sarah, who uses a combination of medications, acupuncture and lots of exercise to counter her pain.

 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this

