
Breaking News
Importing Poverty into America: Devolving Our Nation into Stupid
 Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
 Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
 The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
Fabrication of Ultrastrong 700 Gigapascal Fused Double-walled Carbon Nanotubes
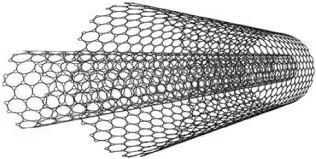
Fused double-walled carbon nanotube (DWNT) fibers were made with a strength of a 700 GPa Young's modulus. This strength was seen in prior experiments, in 2010 and 2011, where electron beams welded DWNTs in microscopic bundles together and the fused bundles had 700 GPa tensile strength. There is now an effort to scale up production of ultrahigh strength material using high temperatures (1700-2300 C) and about 800 atmospheres of pressure instead of an expensive and time-consuming process using high-voltage e-beams. The electron dose available from commercial e-beam facilitaties is so low that processing macroscopic DWNT materials would take months instead of half an hour or less. The same thermal treatment process will enable manufacturing wires that have the highest conductivity of all carbon nanotube wires.



