
Breaking News
 BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
 The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
 Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
 Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Discovery of 'Tendon Stem Cells' Could Revolutionize How We Recover From Injuries
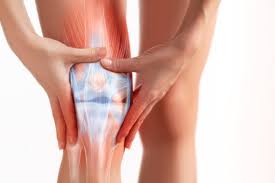
Debilitating tendon injuries may soon be a thing of the past now that researchers have discovered the existence of "tendon stem cells" for the first time.
The buildup of scar tissue makes recovery from torn rotator cuffs, jumper's knee, and other tendon injuries a painful, challenging process, often leading to secondary tendon ruptures.
New research led by Carnegie's Chen-Ming Fan and published in Nature Cell Biology reveals the existence of tendon stem cells that could potentially be harnessed to improve tendon healing and even to avoid surgery.
"Tendons are connective tissue that tether our muscles to our bones," Fan explained. "They improve our stability and facilitate the transfer of force that allows us to move. But they are also particularly susceptible to injury and damage."
Unfortunately, once tendons are injured, they rarely fully recover, which can result in limited mobility and require long-term pain management or even surgery. The culprit is fibrous scars, which disrupt the tissue structure of the tendon.
Working with Carnegie's Tyler Harvey and Sara Flamenco, Fan revealed all of the cell types present in the Patellar tendon, found below the kneecap, including previously undefined tendon stem cells.



