
Breaking News
 BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
 The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
 Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
 Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Motor neurone disease breakthrough as scientists identify cells thought to cause the cruel...
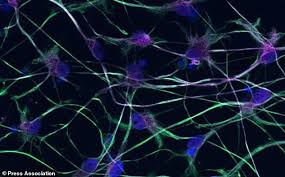
A cure for motor neurone disease – which killed Professor Stephen Hawking – has moved one step closer, scientists believe.
The cruel condition causes signals from motor neurone nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord to fail.
Motor neurones control crucial muscle activity and if they are damaged and break down some patients eventually find it impossible to walk or even speak.
Now researchers have found that another type of brain cell – thought to be harmless – could play a role in the disease, which is also known as ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis).
Tests of cells from skin samples of patients with MND, also known as ALS, showed glial cells can damage motor neurones.
University of St Andrews researchers said glial cells normally support neurones in the brain and spinal cord.



