
Breaking News
6.5x55 Swedish vs. 6.5 Creedmoor: The New 6.5mm Hotness
Best 7mm PRC Ammo: Hunting and Long-Distance Target Shooting
 Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Battery-free biosensor is the smallest one yet
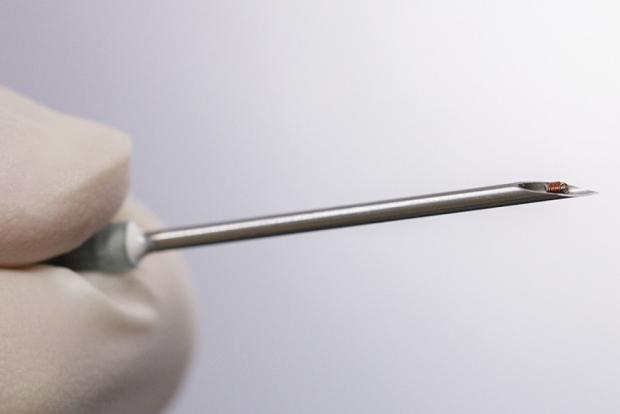
Designed to continuously monitor various bodily processes, externally-powered biosensors are not only smaller than their battery-packing counterparts, but they also don't have to be surgically retrieved for battery-changes.
They typically contain an RFID (radio frequency identification) chip, which transmits data when it's temporarily powered up by the radio signal from an external reader device – that device is in turn held near the implant site on the patient's body. In order to produce a signal that's strong enough to be read, however, the biosensor needs to be relatively large.
Led by Asst. Prof. John Ho, a team at the National University of Singapore recently got around this limitation, by creating a reader that's three times more sensitive than existing devices. As a result, the associated biosensor can be correspondingly smaller.
The current prototype sensor is just 0.9 mm in width, and has been injected under the skin of lab rats utilizing a hypodermic needle. Once implanted, it's able to monitor breathing and heart rates, based on its detection of subtle telltale movements. Once developed further, it is hoped that the technology could do much more.

 The State's Last Stand
The State's Last Stand


