
Breaking News
 The Gaza Gambit: Trump's USD1 And Asset Tokens Will Provide Cradle-To-Grave Financial System
The Gaza Gambit: Trump's USD1 And Asset Tokens Will Provide Cradle-To-Grave Financial System
 Huh? Trump Family Is Jockeying To Replace The Dollar Globally As Their Wealth Soars
Huh? Trump Family Is Jockeying To Replace The Dollar Globally As Their Wealth Soars
 The Gaza Plan's 'Sick Kind of Detachment' and its Dangers for America
The Gaza Plan's 'Sick Kind of Detachment' and its Dangers for America
 Project Artichoke: 70 Years Ago, CIA Discussed Hiding Mind-Control Drugs in Vaccines
Project Artichoke: 70 Years Ago, CIA Discussed Hiding Mind-Control Drugs in Vaccines
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Mice with diabetes "functionally cured" using new stem cell therapy
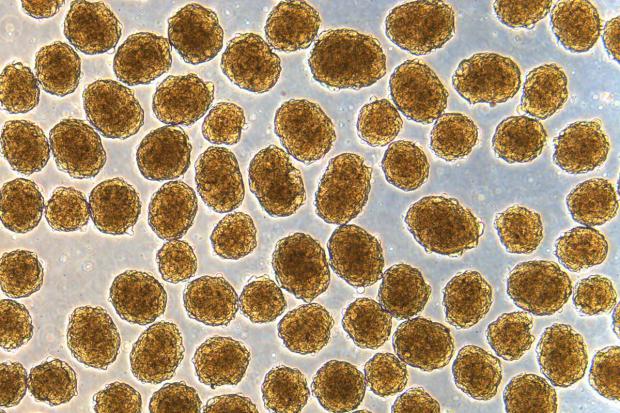
Now, scientists have developed a more efficient method of doing just that, and found that implanting these cells in diabetic mice functionally cured them of the disease.
The study builds on past research by the same team, led by Jeffrey Millman at Washington University. The researchers have previously shown that infusing mice with these cells works to treat diabetes, but the new work has had even more impressive results.
"These mice had very severe diabetes with blood sugar readings of more than 500 milligrams per deciliter of blood — levels that could be fatal for a person — and when we gave the mice the insulin-secreting cells, within two weeks their blood glucose levels had returned to normal and stayed that way for many months," says Millman.
Insulin is normally produced by beta cells in the pancreas, but in people with diabetes these cells don't produce enough of the hormone. The condition is usually managed by directly injecting insulin into the bloodstream when it's needed. But in recent years, researchers have found ways to convert human stem cells into beta cells, which can pick up the slack and produce more insulin.



