
Breaking News
 The Gaza Gambit: Trump's USD1 And Asset Tokens Will Provide Cradle-To-Grave Financial System
The Gaza Gambit: Trump's USD1 And Asset Tokens Will Provide Cradle-To-Grave Financial System
 Huh? Trump Family Is Jockeying To Replace The Dollar Globally As Their Wealth Soars
Huh? Trump Family Is Jockeying To Replace The Dollar Globally As Their Wealth Soars
 The Gaza Plan's 'Sick Kind of Detachment' and its Dangers for America
The Gaza Plan's 'Sick Kind of Detachment' and its Dangers for America
 Project Artichoke: 70 Years Ago, CIA Discussed Hiding Mind-Control Drugs in Vaccines
Project Artichoke: 70 Years Ago, CIA Discussed Hiding Mind-Control Drugs in Vaccines
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Handheld 3D printer used to grow replacement muscle tissue
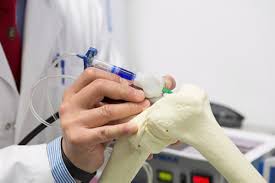
We've actually been hearing a lot about "bioscaffolds" lately.
In a nutshell, they're three-dimensional pieces of biocompatible material that are implanted within the body, and that have a microstructure similar to that of the surrounding tissue. Over time, cells from that tissue migrate into the scaffold, colonizing it and reproducing. Eventually, they entirely replace the material, forming pure muscle, bone, cartilage or other tissue.
That said, pre-producing such bioscaffolds and then implanting them in muscle is quite challenging. With that in mind, scientists at the University of Connecticut developed a prototype handheld 3D printer to do the job.
It starts by depositing a gelatin-based hydrogel directly into the unwanted gap within the muscle. An integrated ultraviolet light causes that gel to cure into a bioscaffold made up of tiny muscle-like fibers, which readily adheres to the adjacent muscle tissue – no sutures are required. Muscle cells then move into the scaffolding.
In lab tests, the device proved to be effective at treating volumetric muscle loss injuries in mice.



