
Breaking News
 Finland to lift full ban on hosting nuclear arms, government says
Finland to lift full ban on hosting nuclear arms, government says
 Trump: I "Have To Be Involved" in Picking Next Iranian Leader
Trump: I "Have To Be Involved" in Picking Next Iranian Leader
 LIVE Emergency Saturday Broadcast: Trump Threatens "Complete Destruction & Certain..."
LIVE Emergency Saturday Broadcast: Trump Threatens "Complete Destruction & Certain..."
 U.S. Military-Industrial Complex Agrees To Quadruple Bomb Production As Operation Epic Fury Rages On
U.S. Military-Industrial Complex Agrees To Quadruple Bomb Production As Operation Epic Fury Rages On
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
High-density hybrid powercapacitors: A new frontier in the energy race
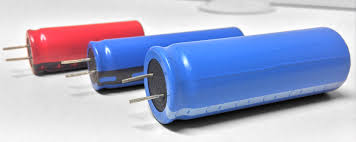
Chinese family-owned company Shenzhen Toomen New Energy is tough to find, at least on the English-language internet, but Belgian electronic engineer Eric Verhulst bumped into Toomen representatives on a tiny stand at the Hannover Messe expo in Germany back in 2018, while looking for next-gen battery solutions for an electric mobility startup he was running.
The Toomen team made a hell of a claim, saying they'd managed to manufacture powerful supercapacitors with the energy density of lithium batteries. "Of course, that's an unbelievable claim," Verhulst told us. "It's a factor of 20 better than what, for example, Maxwell had at the time. So I took my time, went over there, looked at their tests, did some tests myself, and I got convinced this is real. So at the end of 2018, we made an agreement to become their exclusive partner."
According to Verhulst, when he and his team got these "power capacitors" into the lab, they performed even better than they looked on the spec sheet. He tried to break them with charge and discharge rates up to 50C, more than double their rated capacity. They refused to fail. He left them fully charged for months at a time, and found them still well charged when he picked them up again. The University of Munich tested and confirmed their ability to handle temperatures down to -50 ºC (-58 ºF) and up to 45 ºC (113 ºF) without any heating or cooling systems.



