
Breaking News
 China's Nightmarish New Bio Weapon Targets Race and Ethnicity
China's Nightmarish New Bio Weapon Targets Race and Ethnicity
 The Epstein Files Just EXPOSED the AI Mind Control Agenda (2026 Warning)
The Epstein Files Just EXPOSED the AI Mind Control Agenda (2026 Warning)
 Maxwell offers testimony if granted Trump clemency
Maxwell offers testimony if granted Trump clemency
 How RFK Jr's Guidelines Could Change Farming - Joel Salatin
How RFK Jr's Guidelines Could Change Farming - Joel Salatin
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Two new solar cells break records, including highest efficiency ever
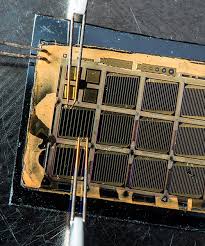
The top honor was claimed by researchers at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), who have developed a new solar cell with an efficiency of 47.1 percent. That makes it the most efficient solar cell of any kind in the world – for now, at least. These records have a tendency to be broken pretty regularly.
The device is what's known as a six-junction III-V solar cell, meaning it's made up of six different types of photoactive layer. Each of these is comprised of various III-V materials, named after their positions on the periodic table, which collect energy from different parts of the light spectrum. In total there are around 140 layers, packed into a solar cell that's thinner than a human hair.
It's also worth noting that the record was broken under light focused to be about 143 times stronger than natural sunlight. While the efficiency of this design is obviously going to drop in real-world uses, the team says that the device could be built with a mirror to focus the sunlight onto the cell.
The team also tested a variation of this cell under light equivalent to one Sun, and it still achieved an efficiency record of 39.2 percent.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

