
Breaking News
 The Self-Sufficiency Myth No One Talks About
The Self-Sufficiency Myth No One Talks About
 We Investigated The Maui Fires and The Cover-Up is Worse Than We Thought | Redacted
We Investigated The Maui Fires and The Cover-Up is Worse Than We Thought | Redacted
 The Amish Secret to Keeping Pests Out of Your Garden Forever
The Amish Secret to Keeping Pests Out of Your Garden Forever
 Scott Ritter: Full-Scale War as Iran Attacks All U.S. Targets
Scott Ritter: Full-Scale War as Iran Attacks All U.S. Targets
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Injection of nanoparticle-based retina restores vision to blind rats
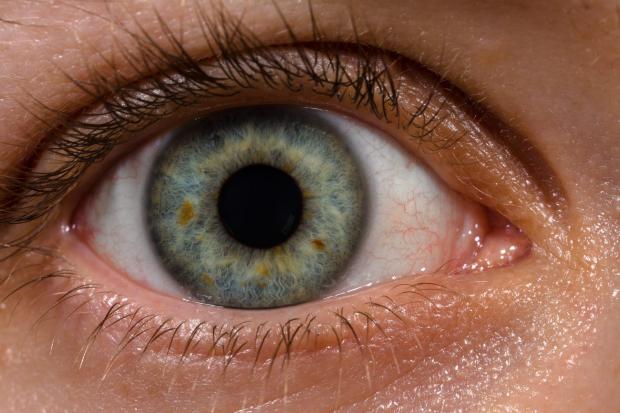
A single injection of nanoparticles was found to create a working artificial retina, restoring vision to blind rodents.
Degenerative age-related vision loss is so common it would be easy to think it simply an unavoidable consequence of getting older. However, a number of innovative research projects have found ways to prevent, or at least slow, this seemingly inevitable process.
A great deal of age-related vision loss is related to a degradation of the retina, so many researchers have worked to develop different kinds of artificial retinas, using electrodes and sensors to replicate retinal functions. However, these prosthetic solutions are not ideal, requiring wiring, cameras and invasive surgery.
Another option to restore retinal function is by using specifically engineered nanoparticles to serve as light-sensitive conduits to retinal neurons. In a newly published study, researchers have demonstrated how conjugated polymer nanoparticles (P3HT-NP) can potentially spread broadly across the sub-retinal space and restore lost vision.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

