
Breaking News
 Escalation of Force: How to Choose the Appropriate Response to Potential Violence
Escalation of Force: How to Choose the Appropriate Response to Potential Violence
 Epstein's Island And The Gateway To The Psychology Of Evil
Epstein's Island And The Gateway To The Psychology Of Evil
 The Epstein Emails Reveal Shadow 9/11 Commission – Exclusive Report!
The Epstein Emails Reveal Shadow 9/11 Commission – Exclusive Report!
 UPDATE: Reps. Massie & Mace Head to DOJ To View Unredacted Epstein Files
UPDATE: Reps. Massie & Mace Head to DOJ To View Unredacted Epstein Files
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
New catalyst rearranges carbon dioxide and water into ethanol fuel
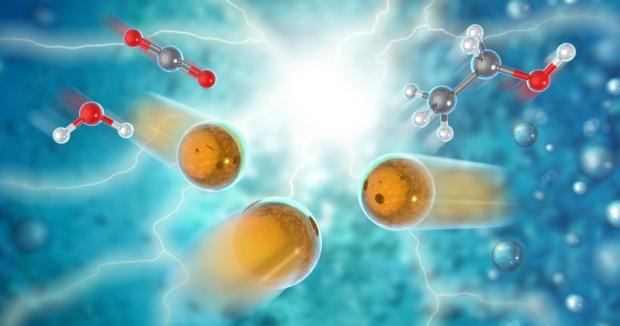
Researchers at the US Dept of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory, working with Northern Illinois University, have discovered a new catalyst that can convert carbon dioxide and water into ethanol with "very high energy efficiency, high selectivity for the desired final product and low cost."
The catalyst is made of atomically dispersed copper on a carbon-powder support, and acts as an electrocatalyst, sitting in a low voltage electric field as water and carbon dioxide are passed over it. The reaction breaks down these molecules, then selectively rearranges them into ethanol with an electrocatalytic selectivity, or "Faradaic efficiency", higher than 90%. The team says this is "much higher than any other reported process."
Once the ethanol is created, it can be used as a fuel additive, or as an intermediate product in the chemical, pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries. Using it as a fuel would be an example of a "circular carbon economy," in which CO2 recaptured from the atmosphere is effectively put back in as it's burned.
If the process is powered by renewable energy, which the researchers say it can be due to its low-temperature, low-pressure operation and easy responsiveness to intermittent power, then great; all you're losing is fresh water, which is its own issue.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

