
Breaking News
 BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
 The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
 Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
 Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Portable X-ray device would let patients check their own bones
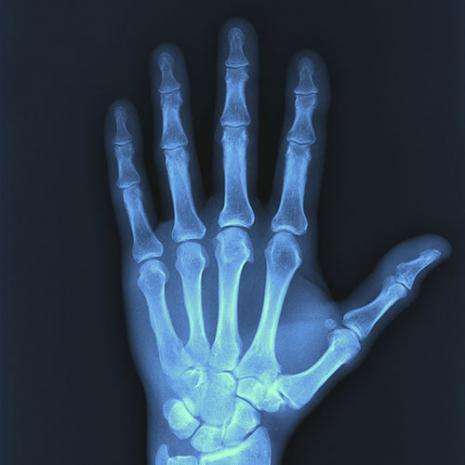
Currently under development at Finland's University of Oulu, the prototype portable X-ray machine measures just 50 by 50 by 130 cm (19.7 by 19.7 by 51.2 in).
Not only is it much smaller than conventional X-ray systems, but because it incorporates built-in radiation shielding, it doesn't have to kept in a lead-lined room, nor does it have to be operated from a separate area. In fact, it utilizes a video screen to guide patients through the process, showing them how and where to place the injured appendage. It then automatically takes the X-rays, and tells the user if a break is detected.
Its instructions – and its imaging voltage – are currently set up for X-raying bones in the palm and ankle. More regions will be added as the system is developed further.
The idea behind the technology is that the relatively inexpensive machines could be set up at locations such as ski resorts or medical clinics, where patients could self-check their injuries to see if a bone was indeed broken. This would reduce the demands placed on larger, pricier, more sophisticated X-ray systems (and their operators), increasing their availability for more important tasks.



