
Breaking News
 No One Does It Like Johnny Carson | Mark Malkoff #470 | The Way I Heard It
No One Does It Like Johnny Carson | Mark Malkoff #470 | The Way I Heard It
 Webb is ready - the open source tool that will decode the Epstein files for EVERYONE
Webb is ready - the open source tool that will decode the Epstein files for EVERYONE
 Trump administration ending Minneapolis immigration Operation Metro Surge
Trump administration ending Minneapolis immigration Operation Metro Surge
 TUMBLER RIDGE MASSACRE: The Trans Shooter Media TRIED TO HIDE...
TUMBLER RIDGE MASSACRE: The Trans Shooter Media TRIED TO HIDE...
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
This Self-Healing Cement Automatically Fills Any Cracks That Form, To Save Energy and Money
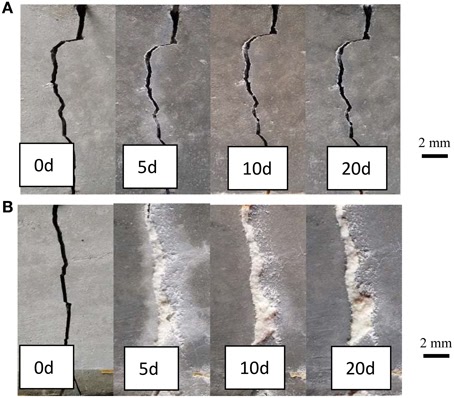
Well, thanks to some very clever folks in England, concrete could be made self-regenerating by the addition of a simple enzyme found in our blood—repairing cracks in the sidewalk, roads, or buildings—saving tons of CO2, as well as millions in dollars, labor hours, and traffic slowdowns.
Recent estimates put the global concrete supply chain at 8% of the world's greenhouse gas emissions, more than three-times that generated from the airline industry. One of the most prevalent human materials also requires the largest supporting infrastructure, from mining, to mixing, to moving, to laying and repairing, it's a massive effort.
Worcester Polytechnic Institute led a project into looking at concrete that repairs itself, which has been hypothesized as possible since the mid-'90s, and which was recently confirmed as possible with bacteria in 2015.



