
Breaking News
 War, Oil And Debt: Which Threats To The US Economy Are Legit?
War, Oil And Debt: Which Threats To The US Economy Are Legit?
 ISIS Attacker Killed by ROTC Students + GDP Crashes to 0.7% + Senate Bans the Digital Dollar
ISIS Attacker Killed by ROTC Students + GDP Crashes to 0.7% + Senate Bans the Digital Dollar
 The Case for Gold: Why It Matters Now | Philip Patrick
The Case for Gold: Why It Matters Now | Philip Patrick
 "This will change HUMANITY!" Intel agencies using nanotech to control our thoughts
"This will change HUMANITY!" Intel agencies using nanotech to control our thoughts
Top Tech News
 Musk Whips Out 'Macrohard' In Disruptive Tesla-xAI Bid To Shaft Software Companies
Musk Whips Out 'Macrohard' In Disruptive Tesla-xAI Bid To Shaft Software Companies
 This Bonkers Folding X-Plane Is One Step Closer to Hitting the Skies
This Bonkers Folding X-Plane Is One Step Closer to Hitting the Skies
 Smart 2-in-1 digital microscope goes desktop or handheld as needed
Smart 2-in-1 digital microscope goes desktop or handheld as needed
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
Inflammation: The Body's 'Fire' Burns Threats, But Things Go Wrong When It Smolders
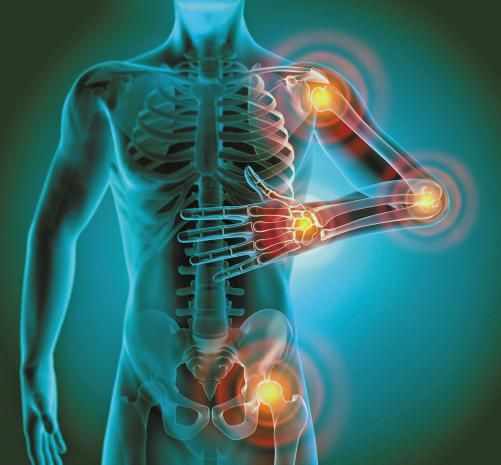
A large-scale study published in Frontiers in Medicine in 2024 showed that among adults in the United States, almost 35 percent had systemic inflammation. Even among healthy individuals (with no evidence of disease), the proportion was about 15 percent.
Chronic inflammation is linked to a wide range of conditions and often "touches on some big diseases," Dr. Frank A. Orlando, the medical director of UF Health Family Medicine–Springhill, told The Epoch Times. And its cause lies in what we eat and do every day.
When the Fire Is Allowed to Smolder
"We need inflammation," Peter Osborne, a clinical nutritionist and chiropractic doctor, told The Epoch Times. The inflammatory response is an essential part of the immune system. When the body is infected or injured, inflammation—often likened to fire—is nature's way of burning away pathogens and repairing damage. Once the threat is eliminated, inflammation should subside. But if the fire continues to smolder, it can become a chronic issue.
Inflammation that persists for more than three months is chronic inflammation, which triggers heart disease, cancer, diabetes, depression, sarcopenia, autoimmune disease, and neurodegenerative disorders, among others.
A review published in Nature Medicine indicated that over 50 percent of deaths can be attributed to inflammation-related diseases.
Chronic inflammation is a significant contributor to many heart diseases. For example, scientists' understanding of atherosclerosis has evolved from viewing it as a passive accumulation of cholesterol to recognizing it as a condition driven by chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation triggers biochemical reactions that lead to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and can cause these plaques to rupture.
A meta-analysis published in The Lancet found that levels of inflammation are linked to increased mortality risk for heart disease, stroke, and several types of cancer. Specifically, every threefold increase in the concentration of C-reactive protein—a standard marker of inflammation—was associated with a 37 percent higher risk of coronary heart disease and a 27 percent higher risk of ischemic stroke.

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

