
Breaking News
 Catherine Fitts: Epstein, CIA Black Budget, the Control Grid, and the Banks' Role in War
Catherine Fitts: Epstein, CIA Black Budget, the Control Grid, and the Banks' Role in War
 "It's a disaster": Germans allowed to use oil and gas to heat their homes again
"It's a disaster": Germans allowed to use oil and gas to heat their homes again
 Victor Davis Hanson: Trump's Cost-Benefit Analysis For Striking Iran
Victor Davis Hanson: Trump's Cost-Benefit Analysis For Striking Iran
 Who is really running the world?
Who is really running the world?
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Artificial intelligence can detect Alzheimer's in brain scans six years before a diagnosis
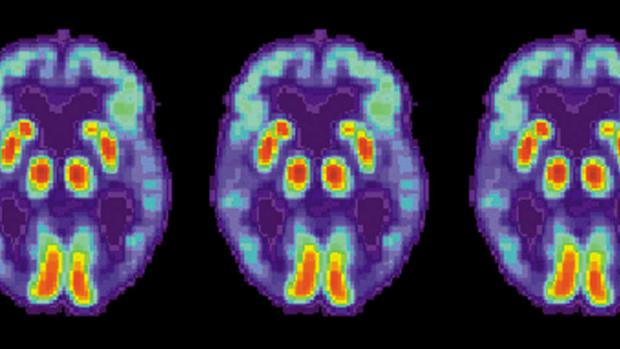
"One of the difficulties with Alzheimer's disease is that by the time all the clinical symptoms manifest and we can make a definitive diagnosis, too many neurons have died, making it essentially irreversible," said Jae Ho Sohn, a resident in the school's Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging and the study's lead researcher, in a statement.
For the study, published in Radiology, Sohn and his team fed a common type of brain scans to a machine-learning algorithm, and it learned to diagnose early-stage Alzheimer's disease about six years before a clinical diagnosis could be made. The AI's diagnostic skills could give doctors a much-needed headstart on treating the degenerative disease.
Sohn and his team focused on PET scans that monitored glucose levels across the brain, because glucose is the primary source of fuel for brain cells. Once the cells become diseased, they eventually stop using glucose, making it an important level to track. However, the changes are subtle—at least to the human eye.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

