
Breaking News
 So long, Paris: US officially leaves landmark climate pact – Trump has formally removed the U.S...
So long, Paris: US officially leaves landmark climate pact – Trump has formally removed the U.S...
 VIDEO: Ilhan Omar Caught In Massive Money Laundering Operation With Fake Winery!
VIDEO: Ilhan Omar Caught In Massive Money Laundering Operation With Fake Winery!
 HISTORIC BOMBSHELL: Trump Federalizes Large Parts Of California After A Year Long Federal...
HISTORIC BOMBSHELL: Trump Federalizes Large Parts Of California After A Year Long Federal...
 Washington Post staffers beg owner Jeff Bezos to spare their jobs amid plans to slash HUNDREDS...
Washington Post staffers beg owner Jeff Bezos to spare their jobs amid plans to slash HUNDREDS...
Top Tech News
 Researchers who discovered the master switch that prevents the human immune system...
Researchers who discovered the master switch that prevents the human immune system...
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
Scientists Find a Switch That Could Stop Osteoporosis, Making Bones Stronger in Old Age
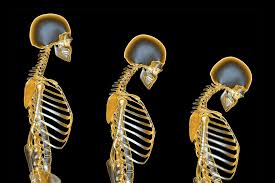
Discovering new targets for drug development is therefore a key step towards better therapies.
In a recent study, scientists at Leipzig University in Germany demonstrated that the G protein receptor called GPR133 plays a central role in building and maintaining healthy bone
"If this receptor is impaired by genetic changes, mice show signs of loss of bone density at an early age—similar to osteoporosis in humans," explains Professor Ines Liebscher, lead investigator of the study published in Nature.
The team was able to significantly increase bone strength in both healthy and osteoporotic mice using the substance AP503, which was recently identified as a stimulator of GPR133.
In bone tissue, GPR133 is activated through the interaction of neighboring bone cells and mechanical strain. This triggers a signal that stimulates bone-forming cells (osteoblasts) and inhibits bone-resorbing cells (osteoclasts).
The result is stronger, more resilient bones.
In the future, it could be used both to further strengthen healthy bones and to rebuild weakened ones—for instance, in cases of osteoporosis in women going through menopause.
Great potential for an aging population
In an earlier study, researchers at Leipzig University had already found that activation with AP503 also strengthens skeletal muscle.
"The newly demonstrated parallel strengthening of bone once again highlights the great potential this receptor holds for medical applications in an aging population," says Dr Juliane Lehmann, lead author of the study and a researcher at the Rudolf Schönheimer Institute of Biochemistry.
The Leipzig research team is already working on several follow-up projects to further investigate the role of GPR133 in the body.



